고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문

이동욱 님의 <스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스> 중 3장 JPA 공부 내용입니다
필기 노트 느낌이라 나만 알아보게 정리함..
* 중간중간 JUnit4로 작성된 부분 JUnit5로 변경해 테스트 진행함
요약 : JPA 왜 쓰는데 / JPA 어노테이션 / Setter 사용 안 함 / Repository / AfterEach (JUnit5) / H2 문법으로 쿼리문 확인 / MySQL 문법으로 쿼리문 확인 / h2 테이블 생성 에러 / JPA Auditing
상속, 1:N등 다양한 객체 모델링을 데이터베이스는 구현할 수 없다. 그러다보니 웹 애플리케이션 개발은 점점 데이터베이스 모델링에만 집중하게 된다. JPA는 이런 문제점을 해결하기 위해 등장하게 된다.
...
개발자는 객체지향적으로 프로그래밍을 하고, JPA가 이를 관계형 데이터베이스에 맞게 SQL을 대신 생성해서 실행한다. 개발자는 항상 객체지향적으로 코드를 표현할 수 있으니 더는 SQL에 종속적인 개발을 하지 않아도 된다.
<스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스> 82page
package com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.domain.posts;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor //기본생성자
@Entity
public class Posts {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(length = 500, nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column(columnDefinition = "TEXT", nullable = false)
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder
public Posts(String title, String content, String author){
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
}(1) @Entity : 테이블과 링크될 클래스임을 명시. 카멜케이스로 작성된 클래스를 언더스코어 네이밍으로 테이블 매칭
(ex) SaVa.java → sa_va table
(2) @Id : 해당테이블의 PK 필드
(3) @GeneratedValue : PK 생성 규칙
- GenetationType.IDENTITY : auto increment
(4) @Column : 설정하지 않아도 해당 클래스의 필드는 모두 칼럼이 되지만, 기본값 외에 추가로 변경이 필요한 옵션이 있으면 사용
- varchar의 경우 기본이 255인데 늘리고 싶으면 length로 늘릴 수 있음
Primary key는 웬만하면 Long 타입, Auto Increment로 설정할 것 (MySQL 기준 bigint)
- 주민등록번호, 복함키로 pk를 설정할 경우 난감한 상황이 발생함
- (1) FK를 맺을 때 다른 테이블에서 복합키 전부를 갖고 있거나, 중간 테이블을 하나 더 둬야 함
- (2) 인덱스에 좋지 않은 영향 끼침
- (3) 유니크한 조건이 변경될 경우 PK 전체 수정
- 주민등록번호, 복합키 등은 유니크 키로 별도 추가하는 걸 추천
Setter 가 없답니다
setter를 무작정 생성하게 되면 해당 클래스의 인스턴스 값들이 언제 어디서 변해야 하는지 코드상으로 명확하게 구분할 수 없어 차후 기능 변경 시 복잡해진다.
그래서 Entity 클래스에서는 절대 Setter 메소드를 만들지 않는다.
대신 해당 필드 값 변경이 필요하면 명확히 그 목적과 의도를 나타낼 수 있는 메소드를 추가해야 한다.
그렇다면 어떻게 값을 채워 DB에 삽입?
기본적인 구조는 생성자를 통해 최종값을 채운 후 DB에 Insert하는 것이며, 값 변경이 필요한 경우 해당 이벤트에 맞는 public 메소드를 호출하여 변경
Setter vs Builder
: Builder를 사용하게 되면 어느 필드에 어떤 값을 넣어야 하는지 명확하게 인지 가능
Repository
package com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.domain.posts;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface PostsRepository extends JpaRepository<Posts, Long> { //JpaRepostory<Entity클래스, PK타입> : Dao라고 불리는 DB Layer 접근자
//CRUD 메소드 자동으로 생성
}
- 프로젝트 규모가 커져 도메인별로 프로젝트를 분리해야 한다면 Entity 클래스와 기본 Repository는 함께 움직여야 하므로 도메인 패키지에서 같이 관리함
(JUnit4) After → (JUnit5) AfterEach
package com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.domain.posts;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.List;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class PostRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
PostsRepository postsRepository;
@AfterEach
public void cleanup(){
// JUnit에서 단위 테스트가 끝날 때마다 수행되는 메소드 지정
// 배포 전 전체 테스트를 수행할 때 테스트간 데이터 침범을 막기 위해 사용
// 여러 테스트가 동시에 수행되면 테스트용 데이터베이스인 H2에 데이터가 그대로 남아 있어 다음 테스트 실행시 테스트가 실패할 수 있음
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void save_content(){
String title = "제목";
String content = "본문";
// save : insert/update 실행
// id 값이 있다면 update 실행, 없다면 insert 실행
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("dh@gmail.com")
.build());
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll();
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
assertThat(posts.getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
assertThat(posts.getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
}만약 쿼리를 보고 싶다면?
# application.properties에 추가 #
spring.jpa.show_sql=true
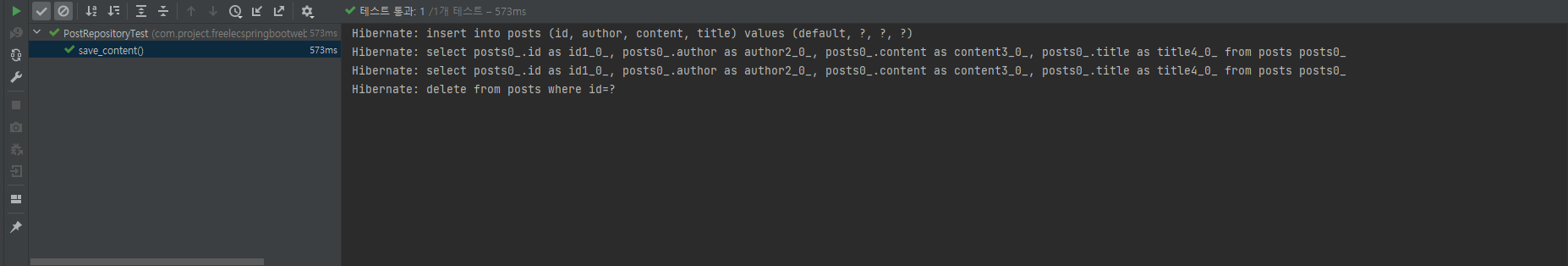
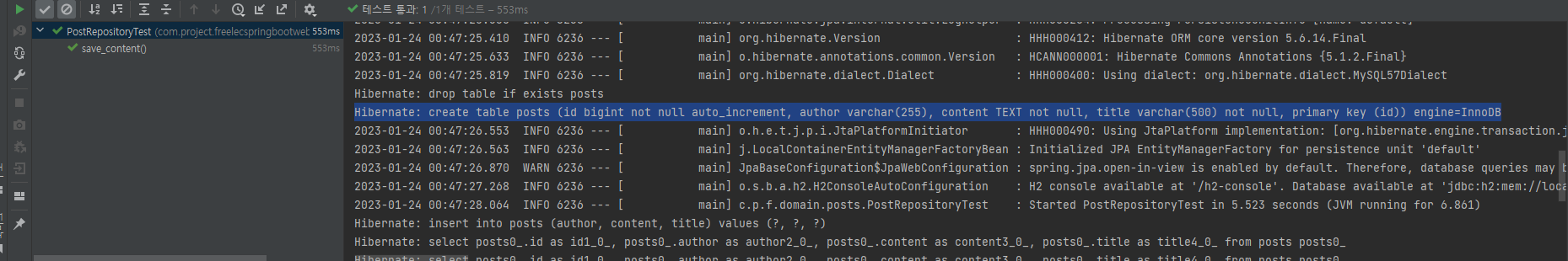
H2 문법 말고 MySQL 문법으로 보고 싶다면?
# application.properties에 추가 #
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL57Dialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.storage_engine=innodb
spring.datasource.hikari.jdbc-url=jdbc:h2:mem://localhost/~/testdb;MODE=MYSQL //자기 h2DB 경로
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
Autowired 사용 지양, 생성자 사용
package com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.web;
import com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.service.posts.PostsService;
import com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.web.dto.PostSaveRequestDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class PostsApiController {
// Controller, Service 모두 Autowired 사용 권장하지 않음
//생성자 주입방식을 권장하므로 final로 선언하고 RequireArgsConstructor 어노테이션으로 Bean객체를 받도록 함
private final PostsService postsService;
@PostMapping("/api/v1/posts")
public Long save(@RequestBody PostSaveRequestDto requestDto){
return postsService.save(requestDto);
}
}
인메모리 데이터베이스 : h2
접근 : http://localhost:포트번호/h2-console
계속 테이블을 생성할 수 없었다.. ddl syntex error 가 발생했다...
나는 책대로 했는디
이러면서 개발자 구글링 실력이 느는 듯
원인은 application.properties MySQL 설정이었다
다른 사람은 좀 더 예전 책으로 했는지 @DataJpaTest, 이 어노테이션이 문제였던 것 같은데 나는 원래 @SpringBootTest로 해서 그 문젠 아니었다
#h2 console 활성화 및 경로 설정
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
#h2 db 설정
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/test;MODE=MySQL;DATABASE_TO_LOWER=TRUE
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
#hibernate 설정
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.storage_engine=innodb
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop

spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/test;MODE=MySQL;DATABASE_TO_LOWER=TRUE
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
이렇게 두 개 수정해서 application.properties에 추가해주니 테이블이 잘 생성됐다 ▶
JPA Auditing으로 생성시간/수정시간 자동화
package com.project.freelecspringbootwebservice.domain;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Getter
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public abstract class BaseTimeEntity {
@CreatedDate
private LocalDateTime createDate;
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime modifiedDate;
}BaseTimeEntity 클래스 : 모든 Entity의 상위 클래스가 되어 Entity들의 createdDate, modifiedDate를 자동으로 관리하는 역할
(1) @MappedSuperclass
: JPA Entity 클래스들이 BaseTimeEntity를 상속할 경우 BaseTimeEntity 내에 작성된 필드들도 칼럼으로 인식
(2) @EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
: BaseTimeEntity 클래스에 Auditing 기능을 포함
(3) @CreatedDate
: Entity가 생성되어 저장될 때 시간이 자동 저장
(4) @LastModifiedDate
: 조회한 Entity의 값을 변경할 때 시간이 자동 저장
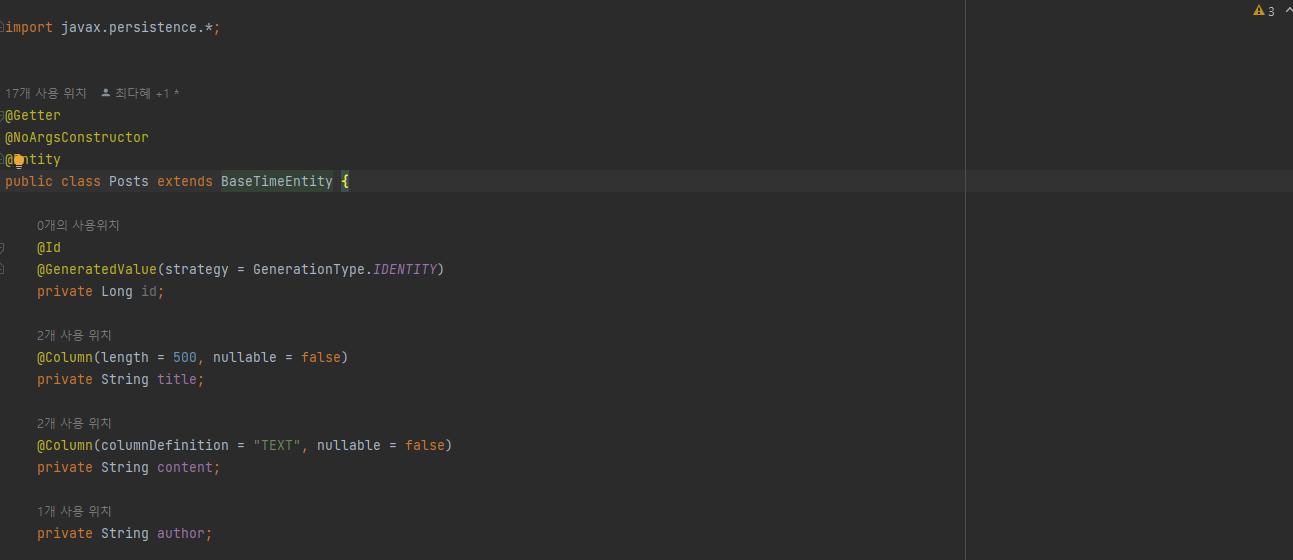
Entity Class에 BaseTimeEntity 상속
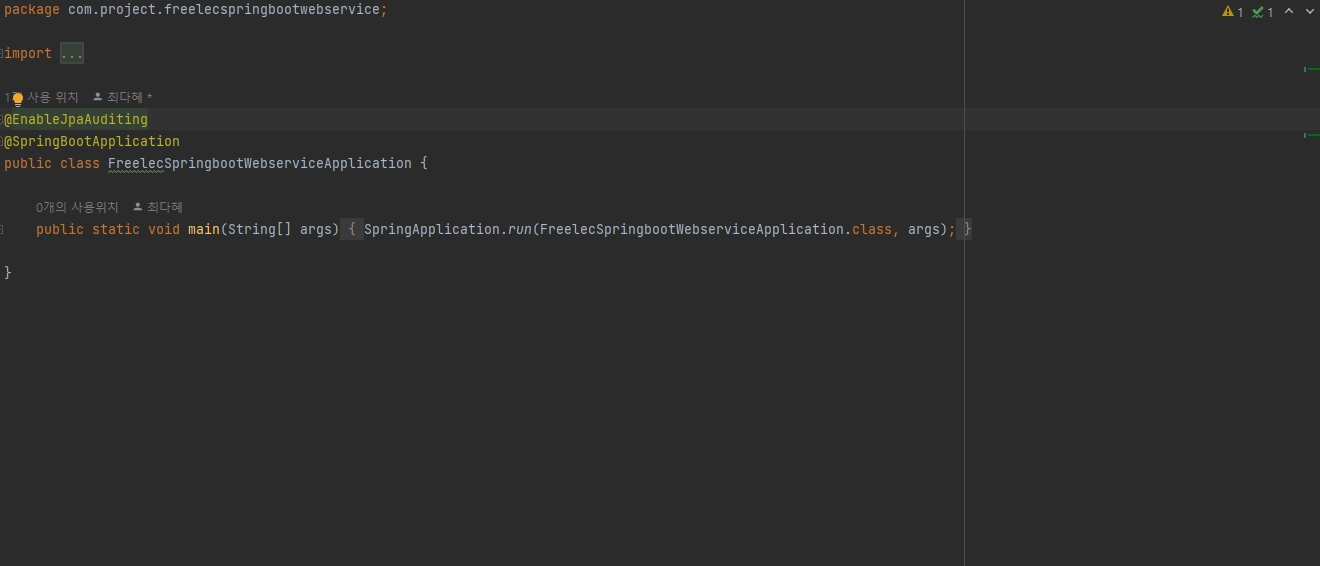
Application에 @EnableJpaAuditing 어노테이션 추가하여 JPA Auditing 활성화
'Web > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스프링부트 핵심가이드] ORM, JPA, 하이버네이트 개념 (0) | 2023.02.22 |
|---|---|
| [S.A혼구웹 / Test] Junit5 사용해보기 (0) | 2023.01.23 |
| [웹개발101] CORS 에러 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
| [웹개발 101] 롬복 어노테이션 정리 :: @Builder / @NoArgsConstructor / @AllArgsConstructor / @Data (0) | 2023.01.14 |




